Data encryption methods play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information from cyber threats. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of data encryption, exploring various techniques and algorithms used to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
From symmetric to asymmetric encryption, hashing algorithms to hybrid techniques, learn how organizations across different industries leverage data encryption to enhance cybersecurity measures.
Overview of Data Encryption Methods

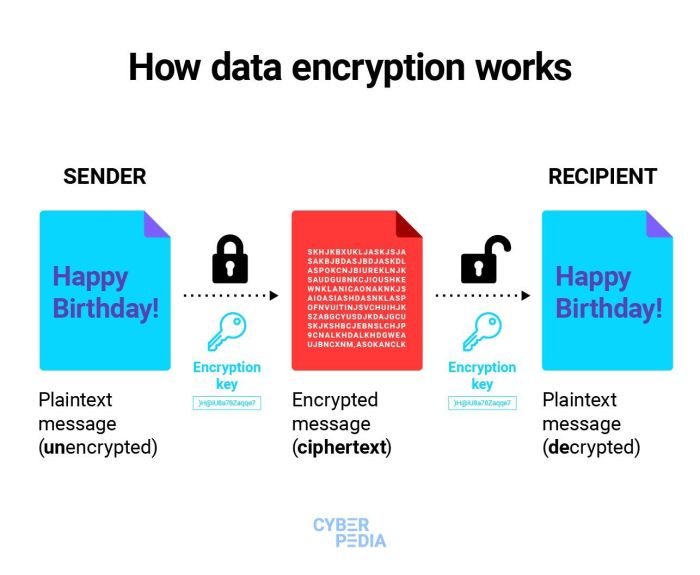
Data encryption plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. By converting data into a secure format that can only be deciphered with the appropriate key, encryption helps prevent data breaches and unauthorized surveillance.
Industries such as finance, healthcare, and government rely heavily on data encryption to safeguard sensitive customer information, medical records, and classified data. Without encryption, these industries would be vulnerable to cyberattacks and data theft, which could have severe consequences for individuals and organizations alike.
The basic principle behind data encryption lies in the use of algorithms to transform plaintext data into ciphertext, making it unreadable to anyone without the decryption key. This process ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure and confidential. Encryption algorithms vary in complexity and strength, with some offering more robust protection than others. It is essential for organizations to choose encryption methods that align with their specific security needs and compliance requirements.
Symmetric Encryption: Data Encryption Methods
Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption of data. This means that the sender and the recipient must both have access to the secret key to communicate securely.
Key Characteristics of Symmetric Encryption
- Simplicity: Symmetric encryption is relatively simple and fast compared to asymmetric encryption.
- Efficiency: It is efficient for encrypting large amounts of data.
- Shared Key: Both parties involved in communication must share the same secret key.
- Security: The security of symmetric encryption relies on the secrecy of the key.
Comparison of Symmetric Key Algorithms
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm known for its security and efficiency. It supports key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits.
- DES (Data Encryption Standard): DES is an older symmetric encryption algorithm that uses a 56-bit key. However, it is considered less secure compared to AES due to its shorter key length.
- 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard): 3DES is a more secure version of DES that applies the DES algorithm three times with different keys. It offers better security but is slower compared to AES.
How Symmetric Encryption Works in Securing Data
Symmetric encryption works by using the same secret key to encrypt and decrypt data. The sender encrypts the data using the secret key before transmitting it, and the recipient uses the same key to decrypt the data upon receiving it. This ensures that only the parties with the secret key can access the original data, providing confidentiality and security in data transmission.
Asymmetric Encryption

Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, is a method of encryption where different keys are used for encrypting and decrypting data. This contrasts with symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both processes. Asymmetric encryption plays a crucial role in data security by providing a secure way for parties to communicate and exchange sensitive information without the need to share a secret key.
Public and Private Keys
In asymmetric encryption, each user has a pair of keys – a public key and a private key. The public key is widely distributed and can be shared with anyone, while the private key is kept secret and known only to the owner. When a sender wants to encrypt a message for a recipient, they use the recipient’s public key. The encrypted message can only be decrypted using the recipient’s private key, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the decrypted data.
Popular Algorithms
Asymmetric encryption relies on complex mathematical algorithms to secure data. Two of the most popular asymmetric encryption algorithms are RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography). RSA is widely used for secure data transmission and digital signatures, while ECC is known for its efficiency in terms of key size and performance. Both algorithms play a key role in securing online communications, financial transactions, and sensitive data storage.
Hashing Algorithms
Hashing algorithms play a crucial role in data encryption by converting input data into a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash value. These algorithms are primarily used for ensuring data integrity and authentication.
Commonly Used Hashing Algorithms
- MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5): MD5 generates a 128-bit hash value and is commonly used for checksums and data integrity verification.
- SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1): SHA-1 produces a 160-bit hash value and is widely utilized in digital signatures and certificates.
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256): SHA-256 creates a 256-bit hash value and is considered more secure than SHA-1 for cryptographic applications.
Hashing algorithms ensure data integrity by generating a unique hash value for specific input data. Any alteration in the input data would result in a different hash value, thereby indicating tampering or corruption. Additionally, these algorithms facilitate authentication by comparing hash values to verify the integrity of transmitted data. By using hashing algorithms, organizations can securely store and transmit sensitive information while detecting unauthorized modifications.
Hybrid Encryption

Hybrid encryption is a method that combines the strengths of symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques to provide a more secure way of protecting sensitive data. This approach addresses the limitations of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption, offering a balanced solution that leverages the benefits of each method.
Advantages of Hybrid Encryption, Data encryption methods
Hybrid encryption offers several advantages over symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods. By combining the two approaches, it maximizes security while maintaining efficiency. Symmetric encryption is fast and efficient for encrypting large amounts of data, while asymmetric encryption provides secure key exchange. Hybrid encryption leverages these strengths, using symmetric encryption to encrypt the data and asymmetric encryption to securely exchange the encryption key.
- Enhanced security: By combining symmetric and asymmetric encryption, hybrid encryption provides a higher level of security compared to using either method alone.
- Efficiency: Symmetric encryption is faster and more efficient for encrypting data, while asymmetric encryption is used for secure key exchange. This combination optimizes performance.
- Secure key exchange: Asymmetric encryption is utilized for securely exchanging the encryption key, mitigating the risks associated with key distribution in symmetric encryption.
Scenarios for Hybrid Encryption
Hybrid encryption is preferred in scenarios where both security and efficiency are paramount. For example, in secure messaging applications, hybrid encryption can be used to ensure that messages are protected during transmission while maintaining a seamless user experience. Additionally, in e-commerce transactions where sensitive financial data is exchanged, hybrid encryption provides a robust security mechanism that protects both data confidentiality and integrity.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of data encryption methods is paramount in today’s digital age. By implementing robust encryption strategies, businesses can fortify their defenses against potential data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring the security and privacy of their valuable information.
When it comes to making informed business decisions, having access to reliable predictive analytics tools can be a game-changer. These tools use historical data to forecast future trends, helping businesses stay ahead of the curve.
Efficiency is key in today’s fast-paced business environment, which is why many companies are turning to reporting automation tools to streamline their processes. These tools automate the generation of reports, saving time and reducing the risk of human error.
For businesses looking to centralize and manage their data effectively, investing in data warehouse solutions is essential. These solutions provide a secure repository for all types of data, making it easier to analyze and extract valuable insights.